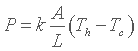www.leguman.ht.st
| HEAD LOSSES |
PUMPS |
CONDUCTION |
©
2001 - 2002.
|
| previous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
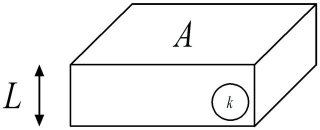
Fourier's law The simplified version of the Fourier's Law gives a relationship between the thermal power P ( W ) which crosses the plate, the temperature difference between the hot face Th and the cold face Tc ( in Kelvin K or Celsius degree °C , it doesn't matter as we will consider temperature differences ), the surface A ( m² ), and the thickness L ( m ).
This law postulates that the thermal power is proportional to the temperature difference Th- Tc , to the surface area A, and inversely proportional to the thickness L . The proportionality factor is called thermal conductivity k and is thus measured in W/(m K); it generally varies with temperature and location, but for what we are concerned these variations are very weak and we will consider thermal conductivity as a constant. It follows :
The following table presents the values of thermal conductivity for the most used materials, at ambient temperature :
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| previous |